This Starbucks SWOT analysis reveals how the largest coffee chain in the world uses its competitive advantages to continue growing so successfully all over the world.
It identifies all the key strengths, weaknesses, opportunities and threats that affect the company the most. If you want to find out more about the SWOT of Starbucks, you’re in the right place.
learn how to do a SWOT analysis.
Company Overview
| Name | Starbucks Corporation |
|---|---|
| Founded | March 31, 1971 |
| Logo |  |
| Industries served | Restaurants (Coffeehouses) |
| Geographic areas served | Worldwide 40,199 coffeehouses |
| Headquarters | Seattle, Washington, United States |
| Current CEO | Brian Niccol |
| Revenue | $36.176 billion (2024) |
| Net Income | $3.761 billion (2024) |
| Employees | 361,000 (2024) |
| Main Competitors | Caribou Coffee Company, Costa Coffee, Dunkin’ Brands Group, Inc., Green Mountain Coffee Roasters, Luckin Coffee Inc., McDonald’s Corporation, Nestlé S.A. and many other restaurant chains and coffeehouses. |
Business Description
Starbucks Corporation’s business overview from the company’s financial report:
“Starbucks is the premier roaster, marketer and retailer of specialty coffee in the world, operating in 81 markets. We purchase and roast high-quality coffees that we sell, along with handcrafted coffee, tea and other beverages and a variety of high-quality food items, including snack offerings, through company-operated stores.
We also sell a variety of coffee and tea products and license our trademarks through other channels such as licensed stores, as well as grocery and foodservice through our Global Coffee Alliance with Nestlé S. A. (“Nestlé”). In addition to our flagship Starbucks Coffee brand, we sell goods and services under the following brands: Teavana, Seattle’s Best Coffee, Evolution Fresh, Ethos, Starbucks Reserve and Princi.
Our objective is to maintain Starbucks standing as one of the most recognized and respected brands in the world. To achieve this, we are continuing the disciplined expansion of our global store base, adding stores in both existing, developed markets such as the U.S., and in newer, higher growth markets such as China, as well as optimizing the mix of company-operated and licensed stores around the world.
In addition, by leveraging the experience gained through our traditional store model, we continue to offer consumers new coffee and other products in a variety of forms, across new categories, diverse channels and alternative store formats. We also believe our Starbucks Global Social Impact strategy, commitments related to ethically sourcing high-quality coffee, contributing positively to the communities we do business in and being an employer of choice are contributors to our objective.
Starbucks® company-operated stores are typically located in high-traffic, high-visibility locations. Our ability to vary the size and format of our stores allows us to locate them in or near a variety of settings, including downtown and suburban retail centers, office buildings, university campuses and in select rural and off-highway locations. We are continuing the expansion of our stores, particularly Drive Thru formats that provide a higher degree of access and convenience, and alternative store formats, which are focused on an elevated Starbucks Experience for our customers.
Starbucks employed approximately 383,000 people worldwide as of September 29, 2019.”[1]
Starbucks SWOT Analysis
| Strengths | Weaknesses |
|---|---|
| 1. Operating efficiency and solid growth leading to superior financial performance 2. Fast growing store network in China 3. The combination of a premium menu, huge range of coffee, and quality customer service provides the best customer experience in the industry 4. Brand awareness and excellent reputation leading to very high customer loyalty 5. Direct ownership of 51% of all Starbucks stores 6. Effective use of the Starbucks Card, store loyalty program and mobile ordering apps to encourage repeat purchases | 1. Overdependence on revenue from the U.S. 2. Slow growth in Europe indicates poor positioning and wrong competitive strategy for those markets 3. High prices when compared to other major coffee-serving chains 4. Overdependence on coffee sales with little ability to influence the volatile price of coffee beans |
| Opportunities | Threats |
|---|---|
| 1. Expansion of ready-to-drink (RTD) coffee products in the U.S. market 2. U.S. spending on food away-from-home is increasing vs. at-home spending 3. Developing Starbucks’ Rewards Program into a reward of choice in the growing electronic payment world 4. Growing demand for specialty coffee, such as cold brew and nitro coffee | 1. The price of coffee beans could significantly rise due to major weather disasters 2. Social trend towards eating healthier food 3. Slowing China’s growth and intensifying competition could affect the chain’s expansion in these country 4. Changes in executive officers’ positions could weaken the company’s management |
Strengths
1. Operating efficiency and strong growth leading to superior financial performance
2019 marked continuing Starbucks growth both financially and physically. The company had yet another great financial year. The company’s revenue grew by 7.2% and 1,932 new stores were opened. Starbucks’ operating profit margin remained above 15% and its cash flow generated US$5.047 billion, despite the company’s enormous expansion.
Figure 1. Starbucks’ consolidated revenue 2013-2019
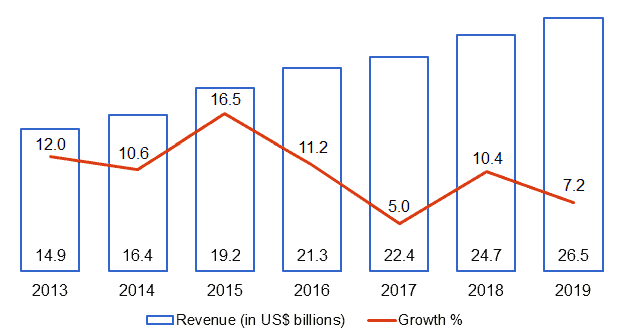
Source: Starbucks’ financial report[1]
Figure 2. Starbucks’ operating profit margin 2012-2019
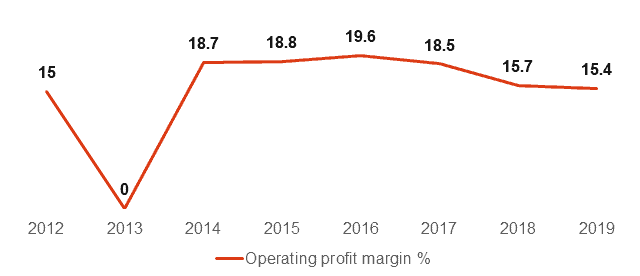
Source: Starbucks’ financial report[1]
Figure 3. Starbucks’ consolidated store count
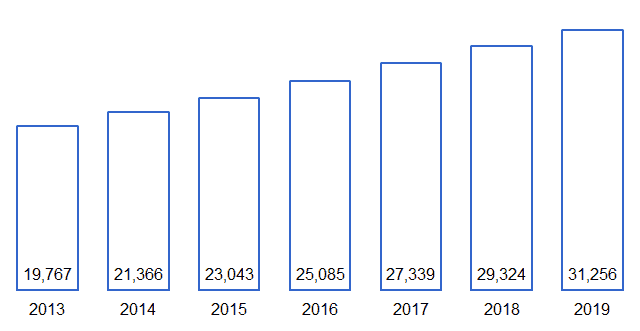
Source: Starbucks’ financial report[1]
The company’s net profit stayed high at $3.594 billion and was actually higher than in 2018 if not including the US$1.4 billion one-time profit increase due to the acquisition of East China joint venture in the previous year.
On the other hand, Starbucks’ balance sheet weakened in 2018 and 2019. The company’s assets decreased, long-term debt increased, which also increased debt-to-asset ratio. Even if the balance sheet should be looked at with caution, the company’s financial position is still as strong as ever.
What does this mean for the company? Despite the fast expansion, company’s significant revenue growth, strong operating and net profits mean that Starbucks is managing its operations very efficiently. The company’s healthy financial numbers provide confidence for investors and allow the company to engage in speculative investments that wouldn’t be feasible otherwise.
2. Fast growing store network in China
Currently, Starbucks has 4,123 restaurants in China, which is more than Costa Coffee’s 449 restaurants (data only from 2018) [2], McDonald’s 3,300 restaurants[3] and Luckin Coffee’s 3,680 restaurants.[4] The number of Starbucks locations has grown significantly over the past few years. In 2011, the company had only 570 coffeehouses in China. Since then it grew its presence to 4,123 locations or 723% in just 8 years.
Figure 4. Number of Starbucks locations in China 2012-2019
| 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Number of locations | 700 | 1,017 | 1,367 | 1,811 | 2,382 | 2,936 | 3,521 | 4,123 |
| Growth over previous year | 22.8% | 45.2% | 34.4% | 32.5% | 31.5% | 23.3% | 19.9% | 17.1% |
Source: Starbucks’ financial report[1]
China will become the second major Starbucks market in the future and is the second fastest growing Starbucks market behind the U.S. already. Most importantly, Starbucks is well positioned to compete in China.
For years Starbucks has been strengthening its tea offerings, which is the favorite Chinese drink. The company currently owns Teavana tea brand and serves brewed tea, single-serve tea, packed tea and other related tea products. Therefore, unlike its rivals, Starbucks is better prepared to satisfy Chinese tastes and to attract Chinese customers to its coffeehouses. In addition to the tea demand, coffee demand is growing in China and Starbucks with its huge coffeehouse network in the country is well positioned to take advantage of this.
3. The combination of a premium menu, huge range of coffee and quality customer service provides the best customer experience in the industry
Unlike other coffee chains, Starbucks is well-known for its quality and excellent customer experience. That’s why the company can charge premium prices and still become the largest coffeehouse chain in the world. To provide the best customer experience Starbucks has to excel at many things, including:
- quality of its coffee and tea;
- menu choices;
- quality of its customer service;
- location and quality of its stores.
Starbucks has always been focused on the quality of its coffee.[5] The company applies strict standards to coffee purchasing, roasting, packaging and distribution. It buys only Arabica beans that are grown at high altitudes. The company tastes each batch of coffee beans at least 3 times before approval. Few of the company’s rivals go through such lengthy quality assurance checks for their coffee ingredients.
Starbucks also provides the most extensive coffee menu in the industry. The company offers more than 50 drinks in each coffeehouse and in total has more than 230 drinks in its product range.[6] By comparison, McDonald’s McCafé, Dunkin’ Donuts and Costa Coffee each offer only more than 20 different drinks.
Starbucks’ high level of customer service, the quality of its stores and their locations are also the pieces that help deliver a competitive advantage in terms of customer experience. The Customer Service Board rates Starbucks at 61st place based on positive customer reviews, while McDonald’s is at 603rd place only.[7]
In addition, Starbucks’ convenient store locations add to the coffee chain’s appeal as customers can seemingly find a Starbucks on almost every corner. In 2019, the company operated 15,049 stores in the U.S. and 16,207 stores internationally, making it the largest coffee chain in the world. Starbucks’ main competitors, McDonald’s, Dunkin’ Donuts and Costa Coffee operated a total of 37,855, 12,871 and 3,821 locations in 2018, respectively. Therefore, except McDonald’s, which actually is more of a fast food chain than coffee selling chain, all other major competitors operate considerably smaller store networks.
Figure 5. Number of stores operating in 2019 and growth over the previous year
| 2019* | Starbucks | McDonald’s | Dunkin’ Donuts | Costa Coffee |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stores | 31,256 | 37,855 | 12,871 | 3,821 |
| Growth over previous year | 6.6% | 1.6% | 2.7% | 8.2% |
Source: The respective companies’ financial reports[1][2][8][9] *McDonald’s, Dunkin’ Donuts and Costa Coffee data is for 2018
Starbucks ability to excel at all of the factors mentioned above allows the chain to provide the best customer experience in the industry and to charge premium prices – an advantage that no other rival can match.
4. Brand awareness and excellent reputation leading to very high customer loyalty
Interbrand, the leading brand evaluation agency, recognizes Starbucks as the 48th most valuable brand in the world and values it at US$11.798 billion.[10] Forbes, which has its own list of the most valuable brands, lists Starbucks as the 35th most valuable brand and values it at US$17 billion.[11] Both companies recognize it as a fast growing brand on their list.
This means that Starbucks brand is one of the most recognizable and reputable in the world. The company’s excellent customer service, premium store design, quality coffee, convenient store locations and best-in-class employment practices have led to a very good brand reputation. Starbucks has been named as one of the “World’s Most Ethical Companies” for 11 years in arrow from 2007 to 2017. [12] Both Starbucks’ brand awareness and reputation have resulted in a very loyal customer base.
Starbucks’s brand popularity and customer loyalty is demonstrated by its huge gift card sales. More than US$9.031 billion were loaded to Starbucks cards in 2019, proving the brand’s popularity among consumers in the U.S. and Canada.[13]
No other coffeehouse chain has such strong brand recognition and customer loyalty as Starbucks, and the company is able to use these factors to its competitive advantage.
5. Direct ownership of 51% of all Starbucks stores
There are a total 31,256 Starbucks locations worldwide, of which 15,834 or 51% are directly managed by the company.[1][3][9] This is considerably more than the direct ownership of both McDonald’s (7.3%) or Dunkin’ Donuts’ (0%) restaurants. The drawbacks of opening and managing directly-owned restaurants over using franchises are the lower operating profit margin and huge capital investments required for new store openings. Yet Starbucks is benefiting from this approach in three ways.
First, the company can tightly control the daily operations of its directly-owned stores and maintain the highest standards, which often get worse during periods of fast expansion. Second, Starbucks receives more revenue from directly-owned stores than from its franchisees. The company therefore receives larger cash flows, which allows further rapid expansion. Third, Starbucks always has the option of increasing its operating margins by selling off directly-owned restaurants to its franchisees.
Few other restaurant chains have this advantage.
6. Effective use of the Starbucks Card, store loyalty program and mobile ordering apps to encourage repeat purchases
The Starbucks Card is a stored value card that offers greater convenience when making a purchase at any Starbucks store. In addition to a faster checkout time, a customer also receives loyalty points, through a related Starbucks Rewards™ program, for every purchase he/she makes using the card.
Every Starbucks customer, who has a Starbucks Card, is automatically enrolled in Starbucks Rewards™ loyalty program, which provides loyalty points, called ‘stars’. Loyalty points can be redeemed for a free product.
To further improve the ordering and purchasing experience, the company has introduced Starbucks mobile app which allows customers to pay for drinks and other in-store purchases with their smartphones. Starbucks mobile app allows to order and pay for a drink or even tip a barista before entering the store. Users can check their Starbucks card balance or how many loyalty points they have just by using the app.
Currently, 46% of all transactions in the U.S. and Canada are made using Starbucks Card and 16% of all transactions in the U.S. are made using a mobile app.[13]
Figure 6. Active Starbucks Rewards Members in the U.S.
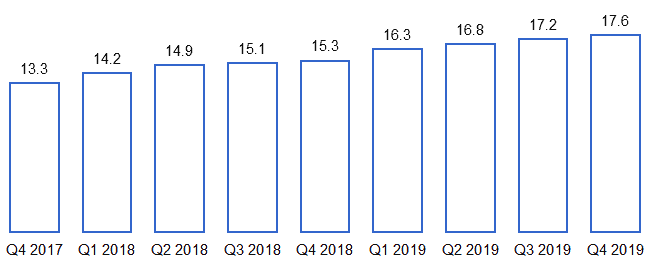
Source: Starbucks Card, Loyalty & Mobile Dashboard [13]
Figure 7. Starbucks Mobile Transactions as % of Total Transactions
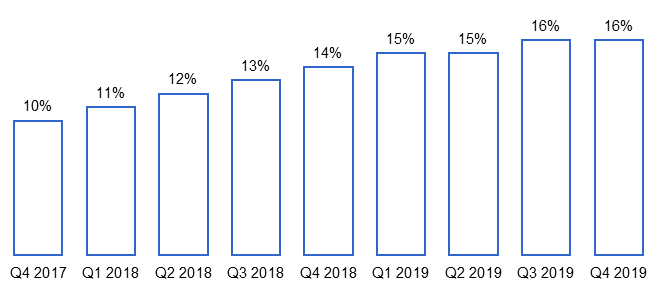
Source: Starbucks Card, Loyalty & Mobile Dashboard [13]
No other company in the U.S. has used a combination of a loyalty program, store card and mobile payment system to attract and retain their customers so successfully.
Weaknesses
1. Overdependence on revenue from the U.S.
Starbucks has been relying on the revenues from the domestic U.S. market significantly. In 2019, the company has earned US$18.623 billion in the U.S and US$7.886 billion internationally. The revenue from the U.S. accounted for 70.3% of the total company’s sales. The U.S. market was always the most important market for Starbucks and will continue to be so for the foreseeable future as no other country generates over 10% of the company’s revenue.
Figure 8. Starbucks’ sources of revenue by country
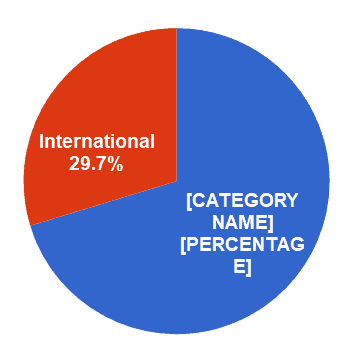
Source: Starbucks’ financial report [1]
In comparison, McDonald’s revenue from the U.S. accounted for only 36.5% of its total sales, indicating a much more geographically diversified sources of revenue.[4]
A high share of revenue coming from one country weakens Starbucks as changes in consumer tastes or political, economic, environmental and legal conditions may severely impact its revenue and operating profit margins.
2. Slow growth in Europe indicates poor positioning and wrong competitive strategy for those markets
In 2019, Starbucks added 1,932 store locations to its worldwide chain. In the UK, the net number of Starbucks’ coffeehouses increased only by 7 stores. While there is no exact number of how many restaurants were added in other European countries, we can guess that the number is around 100. In total, no more than 6% of the total Starbucks restaurants added worldwide were added in Europe in 2019.
Slow growth in Europe is evidence that Starbucks has chosen the wrong strategy to compete with its rivals in Europe. Currently Starbucks is only capable of growing and competing successfully in the U.K., whose culture is the most similar to the U.S. The company’s current strategy is not successful in the rest of Europe.
This weakens the company as it cannot easily grow in one of the largest regions in the world, while some of its competitors generate large shares of the revenues from the European markets. For example, McDonald’s generates around 40% of its revenue from Europe, and Costa Coffee receives over 50%.[2][8]
Starbucks inability to compete with the other large chains or small specialized coffeehouses in Europe results in huge lost sales and slower growth and poorer ability to geographically differentiate its sales.
3. High prices when compared to other major coffee-serving chains
In order to rent premium locations, provide the best quality products, customer service, and an overall excellent customer experience, Starbucks charges premium prices for its coffee. On average, coffee prices in McDonald’s and Dunkin’ Donuts are 35% and 10% lower, respectively, than in Starbucks. The following table compares average coffee prices between Starbucks, McDonald’s and Dunkin Donuts.
Figure 9. Medium size coffee prices in major coffee serving chains in California, the U.S. (in US$)
| Starbucks | McDonald’s | Dunkin’ Donuts | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Coffee | 2.69 | 1.65 | 2.42 |
| Latte | 4.67 | 3.70 | 4.08 |
| Frappuccino | 5.06 | 3.70 | 4.85 |
Source: Fast Food Menu Prices[14][15][16]
The high price of Starbucks’ coffee is a weakness that other chains could exploit, especially if the price of coffee beans is rising. Rising coffee bean prices would increase the overall coffee prices at Starbucks, which could make them too high to pay for even the most loyal Starbucks customers. Currently, Luckin Coffee Inc. is experiencing huge growth in China due to positioning itself as a high quality coffeehouse chain, but with lower coffee prices than at Starbucks.
4. Overdependence on coffee sales with little ability to influence the volatile price of coffee beans
Unlike most of its competitors, Starbucks heavily relies on coffee sales. According to the company’s financial report, beverages make up 74% of the total sales made in its directly-owned stores. This does not include sales of packaged and single-serve coffees and teas, which generate another 1% of the total revenue. While coffee isn’t the only beverage the company offers, it still generates over 50% of the company sales.[1]
Operating mainly the coffeehouse chains and generating most of the revenue by selling coffee isn’t a weakness on its own. The problem is that the price of coffee beans, the company’s main ingredient, is very volatile, often increasing more than 20%, 50% or even 100% in one year. This is a situation over which Starbucks has little control.
Figure 10. The price of coffee beans 2010-2020
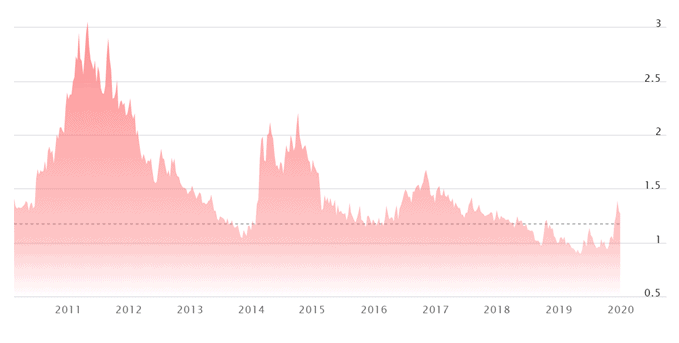
Source: Nasdaq[17]
While rising coffee bean prices affect every coffee retailer, the consequences for them are not as severe as for Starbucks, mainly because coffee sales make up only a small portion of their total revenue.
Opportunities
1. Expansion of ready-to-drink (RTD) coffee products in the U.S. market
According to the Beverage Marketing Corporation Reports, one the fastest growing liquid beverage segment in the U.S. during 2013-2018 was RTD coffees.[18][19][20][21][22][23] In 2018, RTD coffees was the 2nd fastest growing beverage segment in the U.S. beverage industry, growing by an impressive 8.8%.[23] The RTD coffee segment grew 4 times faster than the entire U.S. liquid beverage market, which grew by 2.2% only in 2018.
Figure 11. RTD coffee growth compared to the growth of the whole liquid beverage market in the U.S.
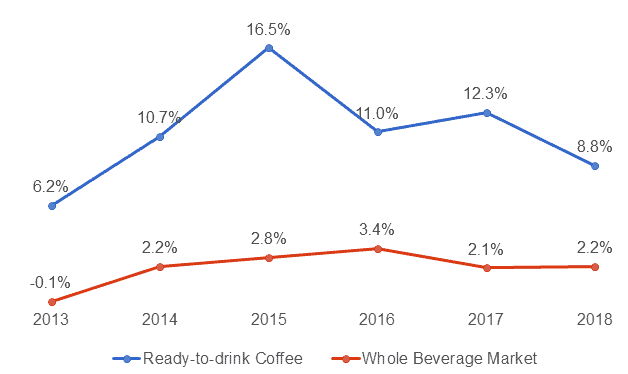
Source: Beverage Marketing Corporation[18][19][20][21][22][23]
Currently, Starbucks is one of the largest RTD coffee brands in the U.S. market. The company offers a variety of espresso, Frappuccino and iced coffee brands. The company’s sales exceed over US$1 billion from RTD beverages. Nonetheless, there’s more room for growth in such a fast growing beverage sector.
Starbucks could expand its cold brew coffee or nitro coffee portfolio to attract more specialty coffee and millennial consumers further strengthening its market position in RTD coffees.
The company could also acquire smaller RTD coffee brands such as Califia Farms, which also offer premium coffee products.
Starbucks has an opportunity to dominate the RTD coffee market in the U.S., while there are still relatively few dominant brands competing in it. The Coca-Cola Company and PepsiCo are strengthening their positions in RTD coffees and there are more brands, which will join soon because RTD coffee market offers lots of potential.
2. U.S. spending on food away-from-home is increasing vs. at-home spending
Starbucks is predominantly a coffeehouse and mainly serves coffee, tea, pastry and some snacks, but it doesn’t offer any meals so it’s not a prime destination for people who go out for a dinner.
Figure 12. Share of consumer dollars spent by daypart
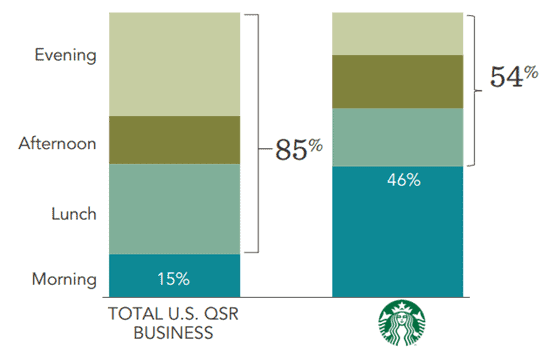
Source: Starbucks’ Strategic Overview
On average, people spend most of their money at Starbucks when they buy their morning coffee, breakfast and some light lunch. Compared to an average U.S. spender, Starbucks doesn’t attract enough people during the evening, mainly because it doesn’t have suitable offerings on its menu.
That’s why Starbucks should expand its food offerings to accommodate diners. It offers quality pastries, sandwiches, yoghurt, fruits and now salads to satisfy lunch eaters. However, this is only a small step in the right direction and Starbucks still needs to transform its menu to become more suitable for casual diners, especially when the U.S. spending on food away-from-home is increasing.
Figure 13. The U.S. food spend at-home vs. away-from-home spending
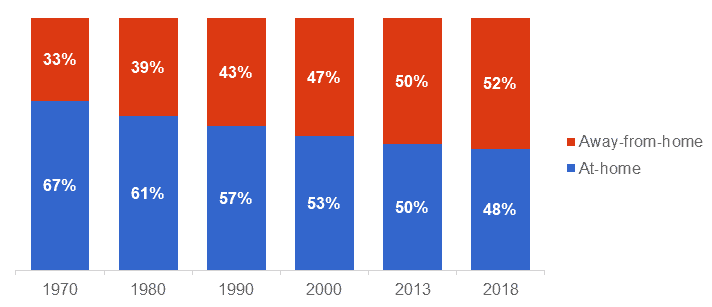
Source: USDA[24]
Starbucks could also diversify its product portfolio by acquiring a small growing restaurant chain or by introducing its own restaurant chain where the primary product would be food. The company already has capabilities and competence in managing and growing a coffeehouse chain successfully.
3. Developing Starbucks’ Rewards system into a reward of choice for other retailers in the growing electronic payment world
Starbucks experienced huge success when it introduced its loyalty program, offering Starbucks Rewards as incentives for buying with Starbucks Cards or using their mobile app. According to the company, Starbucks Rewards (SR) members spend 3 times more than non-SR customers. Starbucks customers are attracted to the company’s loyalty program because it offers useful and convenient rewards for products that are consumed daily.
Figure 14. Active Starbucks Rewards Members in the U.S.
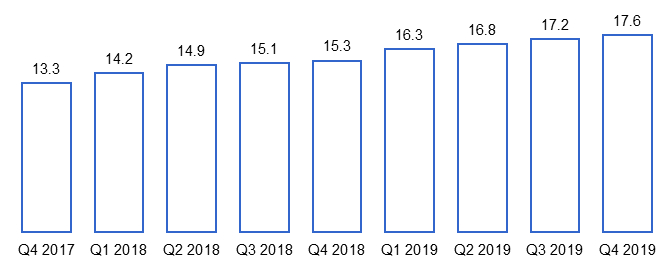
Source: Starbucks Card, Loyalty & Mobile Dashboard [13]
Currently, there are more than 17.6 million active SR members. If the same growth rate of SR members continues, the company will have 20 million SR members by 2022. This means that Starbucks Rewards will become an attractive choice of reward for other companies that use loyalty programs to attract customers.
Starbucks, which already has a well-functioning mobile payment system integrated with its SR, is well positioned to take advantage of the growth in electronic payment systems. Businesses which offer loyalty programs can easily integrate Starbucks Rewards system with their payment systems and offer Starbucks gifts as a reward for their own customers’ loyalty. That would greatly benefit both the businesses integrating SR into their system and Starbucks itself, allowing it to increase its SR member base faster and more easily.
4. Growing demand for specialty coffee, such as cold brew and nitro coffee
The demand for specialty coffee is on the rise in the U.S. The total value of the U.S. coffee market is estimated to be around US$47.5 billion with specialty coffee comprising 60% of the market. [25][26]
One of the areas that see specific fast growth are cold brew and nitro coffees. According to the research done by Grand View Research, the market for cold brew coffee was worth US$339.7 million in the U.S. in 2018.[27] It is expected to grow by 25.1% for the next 6 years and should be worth US$1.63 billion by 2025.[28]
Starbucks currently offers a variety of cold brew coffees in its menu, but should expand its variety of premium cold brew coffees and offer them in all of the stores.
Nitro coffee is a coffee drink infused with nitrogen. It is served from the tap and is a new generation coffee drink. Starbucks currently offers only a few variations of the drink and only in some of its stores.
Starbucks, which is a mainstream coffee shop, could expand its specialty coffee menu that would focus more on quality of the coffee and would attract artisan coffee drinkers. The company could also offer a wider variety of cold brew coffee drinks to be sold in supermarkets.
Threats
1. The price of coffee beans could significantly rise due to major weather disasters
Coffee generates about 74% of the company’s total sales and coffee beans are the major raw material used in its production. Therefore, Starbucks profit margins are dependent, to some extent, on the price of coffee beans, which have been very volatile in the past.
Coffee bean prices topped US$3 per pound in 2011, which was the highest price in 34 years. In 2019, coffee prices dropped below US$0.91 per pound and were the lowest in over 10 years, but this trend is unlikely to be sustained.
Figure 15. The price of coffee beans 2010-2020
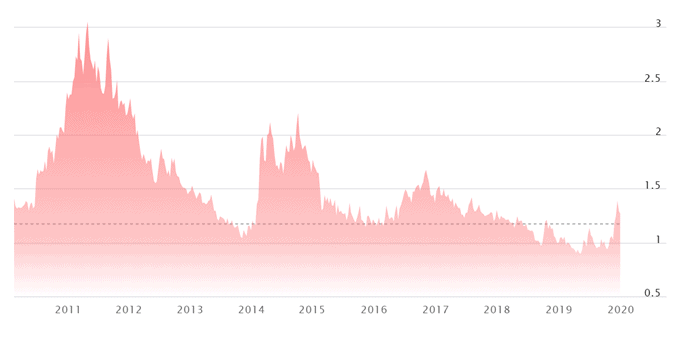
Source: Nasdaq[17]
The major reasons for such price volatility are droughts, unusually high or low temperatures and many other weather disasters in Brazil and other coffee-growing countries. In addition to those factors, growing demand for coffee in China has increased competition for the best quality coffee beans and has pushed the prices up significantly.
Starbucks uses many agreements with its suppliers in order to buy coffee on a fixed-price basis, however such agreements only prevent price increases for a short-time. Every few years the price of coffee beans generally rises and companies like Starbucks have to find ways to pass that increase on to customers or accept a lower profit margin. So far, Starbucks has been successful in coping with high coffee prices, but there’s no guarantee this won’t affect the company in the long-term.
2. Social trend towards eating healthier food
The trend towards healthier eating has hit the largest fast food restaurant chains, such as McDonald’s, Burger King, KFC and Subway, hard. These companies have received much criticism for contributing to obesity. According to Calorie King, the McDonald’s Cheeseburger, which contains around 300 calories,[29] equates to Starbucks Pumpkin Spice Latte with Soy Milk, without whipped cream, grande size drink, which contains 310 calories.[30] While, Starbucks has not received any criticism for its contribution to the obesity of the U.S. citizens, the company recognizes this threat in its financial report:
“Particularly in the U.S., there is increasing consumer awareness of health risks, including obesity, as well as increased consumer litigation based on alleged adverse health impacts of consumption of various food and beverage products. While we have a variety of beverage and food items, including items that are coffee-free and have reduced calories, an unfavorable report on the health effects of caffeine or other compounds present in our products, whether accurate or not, imposition of additional taxes on certain types of food and beverage components, or negative publicity or litigation arising from certain health risks could significantly reduce the demand for our beverages and food products and could materially harm our business and results of operations.”[1]
This might change in the future and Starbucks could suffer from the healthy eating trend like other restaurant chains serving calorie rich food.
3. Slowing China’s growth and intensifying competition could affect the chain’s expansion in these country
China is the fastest growing and the second largest Starbucks market. The company is increasingly dependent on the success and growth of its coffeehouse network in China. The company has 4,123 coffeehouses in the country. In 2019, a third of all the restaurants opened by Starbucks were in China.[1]
Currently, China’s economic growth is the lowest in 29 years.[31] In 2019, China’s economy grew only by 6.1% and the forecast projects that the economy will grow at an even slower pace in 2020. This means that consumer’s disposable income will not grow as fast and they will have less money to spend on an already high priced Starbucks’ drinks.
Rivalry in China’s coffee serving restaurant market is also intensifying. Despite the international rivals, like McDonald’s, which either grow fast in the country already or introduce plans to expand their growth in China, domestic competitors are attempting to establish themselves as serious competitors to Starbucks as well. One of the main domestic competitors is Luckin Coffee Inc. As of Q3 2019, the company had 3,680 coffeehouses in China, a growth of 209.5% from 1,189 stores in Q3 2018.[32] Just in one year, the company opened 2,491 stores and that growth in China is much faster than what Starbucks could ever achieve. In 2020, the company will outgrow Starbucks restaurant chain in China’s market and could pose a serious threat to Starbucks’ growth prospects as the coffee quality is comparable and the prices are lower than at Starbucks’ stores.[33] Luckin Coffee is only one of the several growing domestic coffeehouse chains in China.
The increasing competition from the local and international rivals and slowing growth of China’s economy will negatively affect Starbucks’ expansion in the country.
4. Changes in executive officers’ positions could weaken the company’s management
Every company’s success strongly depends on how it is managed. Starbucks is no exception. Since Starbucks Corporation’s inception in 1985, the company has relied upon CEO Howard Schultz, who has managed to grow the corporation into becoming one of the largest restaurant chains in the world. Many other top executives have been with the company for more than 10 years and have helped the company to reach its current level of success.
Figure 16. Top Executive Officers of Starbucks
| Name | Age | Position |
|---|---|---|
| Kevin R. Johnson | 59 | president and chief executive officer |
| Rosalind G. Brewer | 57 | group president, Americas and chief operating officer |
| Cliff Burrows | 60 | group president, Siren Retail |
| John Culver | 59 | group president, International, Channel Development and Global Coffee & Tea |
| Rachel A. Gonzalez | 50 | executive vice president, general counsel and secretary |
| Patrick J. Grismer | 57 | executive vice president, chief financial officer |
| Lucy Lee Helm | 62 | executive vice president, chief partner officer |
| John Kelly | 53 | executive vice president, Global Public Affairs and Social Impact |
Source: Starbucks’ financial report[1]
The threat is that many of their top executives may retire sooner rather than later due to their age and this could weaken the company’s management capabilities. Starbucks will have to fill vacant positions with new executives, whose skills and abilities may not meet the expectations. This already happened when Howard Schultz left the Starbucks CEO position in 2000. He returned in 2008, because Starbucks’ financial position and its culture weakened due to poor management.
In April 2017, Starbucks’ CEO Howard Schultz retired again. Kevin R. Johnson, Starbucks previous chief operating officer assumed CEO duties. This and many other impending retirements could negatively affect Starbucks’ management capabilities in the future.
Summary
Starbucks has experienced a significant growth over the last few years and this trend should continue in the near future.
The company still has lots of growth potential in new and current markets. The combination of all Starbucks’ strengths will allow the company to successfully compete with rivals and grow fast.
Starbucks should further strengthen its digital capabilities, operating efficiency and maintain the current quality of ‘Starbucks experience’. All of these strengths will help the company in the future.
As for the weaknesses, few of them can significantly damage company or its sales. Starbucks should diversify geographically and expand in Europe. Product diversification would also help to increase the revenue and eliminate strong dependence on coffee sales.
Opportunities are well-known for Starbucks and the company already pursues some of them. Starbucks should really put efforts in becoming more of a dining place than just a coffee shop. That would open new opportunities and growth for the company.
Threats do not pose immediate danger for Starbucks. The company uses various contracts and other agreements to shield against the volatile prices of coffee beans. Other threats can be easily eliminated in the future.
Sources
- Starbucks Corporation (2021) annual report. Available at: https://s22.q4cdn.com/869488222/files/doc_financials/2021/ar/Starbucks-Fiscal-2021-Annual-Report.pdf Accessed July 14, 2022
- Whitbread PLC (2018). Annual Report and Accounts 2017/18. Available at: https://www.whitbread.co.uk/~/media/Files/W/Whitbread/report-and%20presentations/2018/Whitbread%20Interactive%202018.pdf Accessed January 27, 2020
- McDonald’s Corporation (2019). McDonald’s in China. Available at: https://www.mcdonalds.com.cn/index/McD/mcdonalds-china/MCD-in-China-2 Accessed January 27, 2020
- Luckin Coffee Inc. (2019). Luckin Coffee Inc. Announces Unaudited Third Quarter 2019 Financial Results. Available at: http://investor.luckincoffee.com/static-files/e228e5f9-e47f-47e4-b8dd-f1cabe870ebb Accessed January 27, 2020
- Starbucks (2020). Quality. Available at: https://www.starbucks.ca/coffee/ethical-sourcing/coffee-quality Accessed January 27, 2020
- Starbucks (2020). Explore Our Menu. Available at: https://www.starbucks.com/menu Accessed January 27, 2020
- Customer Service Scoreboard (2020). The Leaderboard. Available at: http://www.customerservicescoreboard.com/ Accessed January 27, 2020
- McDonald’s Corporation (2019). Form 10-K For the fiscal year ended December 31, 2018. Available at http://d18rn0p25nwr6d.cloudfront.net/CIK-0000063908/94ad07bd-66c3-433c-a81e-94f1587b0ed8.pdf Accessed January 27, 2020
- Dunkin Brands (2018). Annual Report 2018. Available at: http://investor.dunkinbrands.com/static-files/7a1e2ad8-3f4e-49d1-9126-1e2b7c43b012 Accessed January 27, 2020
- Interbrand (2020). Best Global Brands 2019. Rankings. Available at: http://interbrand.com/best-brands/best-global-brands/2019/ranking/ Accessed January 27, 2020
- Forbes (2020). The World’s Most Valuable Brands. Available at: http://www.forbes.com/powerful-brands/list/ Accessed January 27, 2020
- Starbucks (2020). Starbucks Company Recognition. Available at: https://www.starbucks.com/about-us/company-information/starbucks-company-recognition Accessed January 27, 2020
- Starbucks (2018). Starbucks Card, Loyalty & Mobile Dashboard. Available at: https://s22.q4cdn.com/869488222/files/doc_financials/quarterly/2019/q4/FY19_Q4_Digital-Dashboard_Final.pdf Accessed January 27, 2020
- Fast Food Menu Prices (2020). Starbucks Prices. Available at: http://www.fastfoodmenuprices.com/starbucks-prices/ Accessed January 27, 2020
- Fast Food Menu Prices (2020). McDonald’s Prices. Available at: http://www.fastfoodmenuprices.com/mcdonalds-prices/ Accessed January 27, 2020
- Fast Food Menu Prices (2020). Dunkin’ Donuts Prices. Available at: http://www.fastfoodmenuprices.com/dunkin-donuts-prices/ Accessed January 27, 2020
- NASDAQ (2020). Coffee. Available at: https://www.nasdaq.com/market-activity/commodities/kt%3Anmx?timeframe=10y Accessed January 27, 2020
- Beverage Marketing Corporation (2014). Press Release: The U.S. Liquid Refreshment Beverage Market Remained Flat in 2013. Available at: http://www.beveragemarketing.com/news-detail.asp?id=299 Accessed January 27, 2020
- Beverage Marketing Corporation (2015). Press Release: The U.S. Liquid Refreshment Beverage Marketing Enlarged in 2014, Reports Beverage Marketing Corporation. Available at: http://www.beveragemarketing.com/news-detail.asp?id=335 Accessed January 27, 2020
- Beverage Marketing Corporation (2016). Press Release: The U.S. Liquid Refreshment Beverage Market Accelerated in 2015, Reports Beverage Marketing Corporation. Available at: http://www.beveragemarketing.com/news-detail.asp?id=382 Accessed January 27, 2020
- Beverage Marketing Corporation (2017). Press Release: The U.S. Liquid Refreshment Beverage Market Accelerated Again in 2016. Available at: http://www.beveragemarketing.com/news-detail.asp?id=439 Accessed January 27, 2020
- Beverage Marketing Corporation (2018). Press Release: U.S. Liquid Refreshment Beverage Market Retail Dollars and Volume Both Grew in 2017, Reports Beverage Marketing Corporation. Available at: https://www.beveragemarketing.com/news-detail.asp?id=485 Accessed January 27, 2020
- Beverage Marketing Corporation (2019). Press Release: U.S. Liquid Refreshment Beverage Market Retail Dollars and Volume Growth Accelerated in 2018. Available at: https://www.beveragemarketing.com/news-detail.asp?id=554 Accessed January 27, 2020
- United Stated Department of Agriculture (2018). America’s Eating Habits: Food Away From Home. Available at: https://www.ers.usda.gov/webdocs/publications/90228/eib-196_ch3.pdf?v=8116.5 Accessed January 27, 2020
- Lock, S. at Statista (2019). Size of the coffee shop market in the United States in 2018 and 2019. Available at: https://www.statista.com/statistics/1032200/coffee-shop-industry-market-size-us/ Accessed January 27, 2020
- Brown, N. at Daily Coffee News (2019). 2019 Coffee and Beverage Trends: Inside the NCA’s Annual Report. Available at: https://dailycoffeenews.com/2019/03/11/2019-coffee-and-beverage-trends-inside-the-ncas-annual-report/ Accessed January 27, 2020
- Grand View Research (2019). Cold Brew Coffee Market Size, Share & Trends Analysis Report. Available at: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/industry-analysis/cold-brew-coffee-market Accessed January 27, 2020
- Grand View Research (2019). Cold Brew Coffee Market Worth $1.63 Billion By 2025 Available at: https://www.grandviewresearch.com/press-release/global-cold-brew-coffee-market Accessed January 27, 2020
- Calorie King (2020). McDonald’s Cheeseburger. Available at: http://www.calorieking.com/foods/calories-in-sandwiches-burgers-burger-cheeseburger_f-ZmlkPTEwMDk0Ng.html Accessed January 27, 2020
- Calorie King (2020). Starbucks Pumpkin Spice Latte with Soy Milk, without whipped cream. Available at: https://www.calorieking.com/us/en/foods/f/calories-in-beverages-pumpkin-spice-latte-with-soy-milk-without-whipped-cream/–37HK4kTx6OEqb0LEkZXA Accessed January 27, 2020
- Trading Economics (2020). China GDP Growth Rate. Available at: http://www.tradingeconomics.com/china/gdp-growth-annual Accessed January 27, 2020
- Luckin Coffee Inc. (2019). Luckin Coffee Inc. Announces Unaudited Third Quarter 2019 Financial Results. Available at: http://investor.luckincoffee.com/static-files/e228e5f9-e47f-47e4-b8dd-f1cabe870ebb Accessed January 27, 2020
- Bai, T. at Pan daily (2019). The Coffee Chain that Came Out of Nowhere with the Potential to Beat Starbucks in China. Available at: https://pandaily.com/the-coffee-chain-that-came-out-of-nowhere-with-the-potential-to-beat-starbucks-in-china/ Accessed January 27, 2020

